LSP: Mason and LspSettings
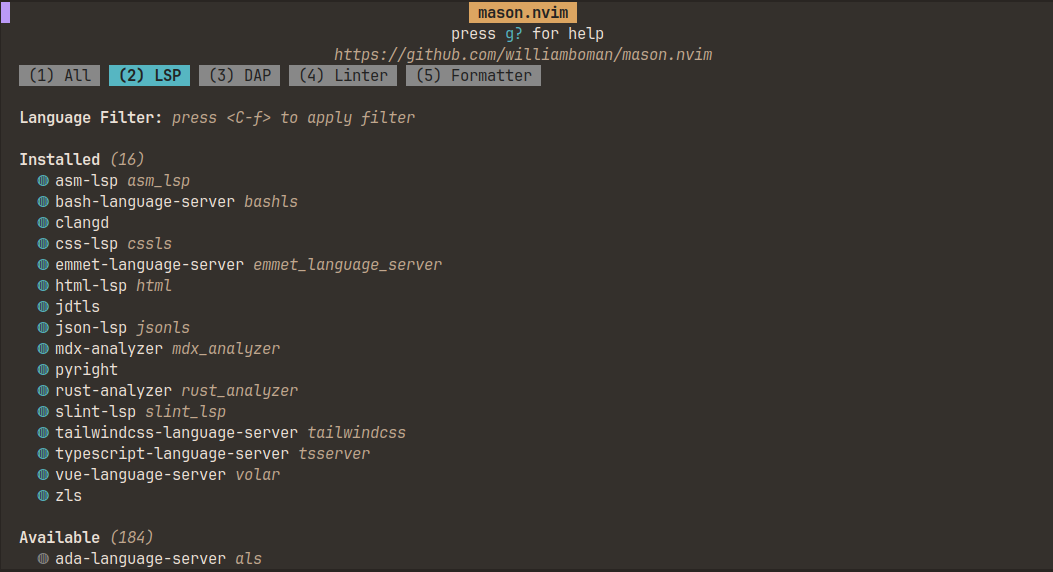
with Mason.nvim you can easily and quickly install an lsp
Example with vtsls
Installation
:LspInstall vtsls
What to do if mason is not supported on your platform
you will have to configure lsp manually from the file ~/.config/nvim/lua/userconfig/lsp.lua
Manual Installation
lsp.lua
vim.lsp.config('vtsls', {
capabilities = capabilities,
on_attach = on_attach
})Manual Configuration
You can modify everything you want: commands, root dirs, settings, etc.
lsp.lua
vim.lsp.config('vtsls', {
cmd = { "vtsls", "--stdio" },
filetypes = { "javascript", "javascriptreact", "javascript.jsx", "typescript", "typescriptreact", "typescript.tsx" },
init_options = {
hostInfo = "neovim"
},
settings = {
javascript = {
inlayHints = {
enumMemberValues = { enabled = true },
functionLikeReturnTypes = { enabled = true },
parameterNames = { enabled = "literals" }, -- "none" | "literals" | "all"
parameterTypes = { enabled = true },
propertyDeclarationTypes = { enabled = true },
variableTypes = { enabled = true },
},
},
typescript = {
inlayHints = {
enumMemberValues = { enabled = true },
functionLikeReturnTypes = { enabled = true },
parameterNames = { enabled = "literals" }, -- "none" | "literals" | "all"
parameterTypes = { enabled = true },
propertyDeclarationTypes = { enabled = true },
variableTypes = { enabled = true },
},
},
},
single_file_support = true,
root_dir = root_dir = function(bufnr, on_dir)
local fname = vim.api.nvim_buf_get_name(bufnr)
on_dir(util.root_pattern("package.json", "tsconfig.json", "jsconfig.json", ".git")(fname))
end,
on_attach = on_attach
})Formatters
Many lsp's like rust analyzer or zls come with default formatters which can be called with the command :lua vim.lsp.buf.format()
For cases where there is no default formatter you can use Mason to install formatters and null-ls will take care of assigning them
Example with Python
:MasonInstall autopep8
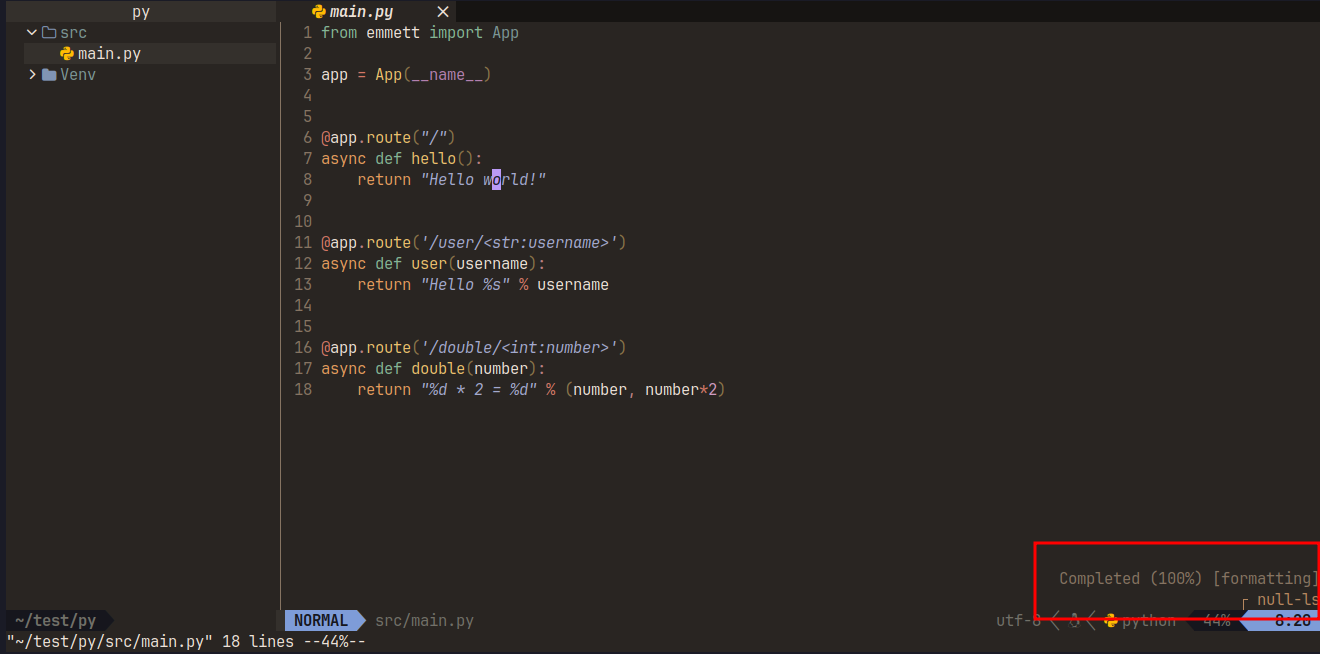
With null-ls:
Without null-ls:
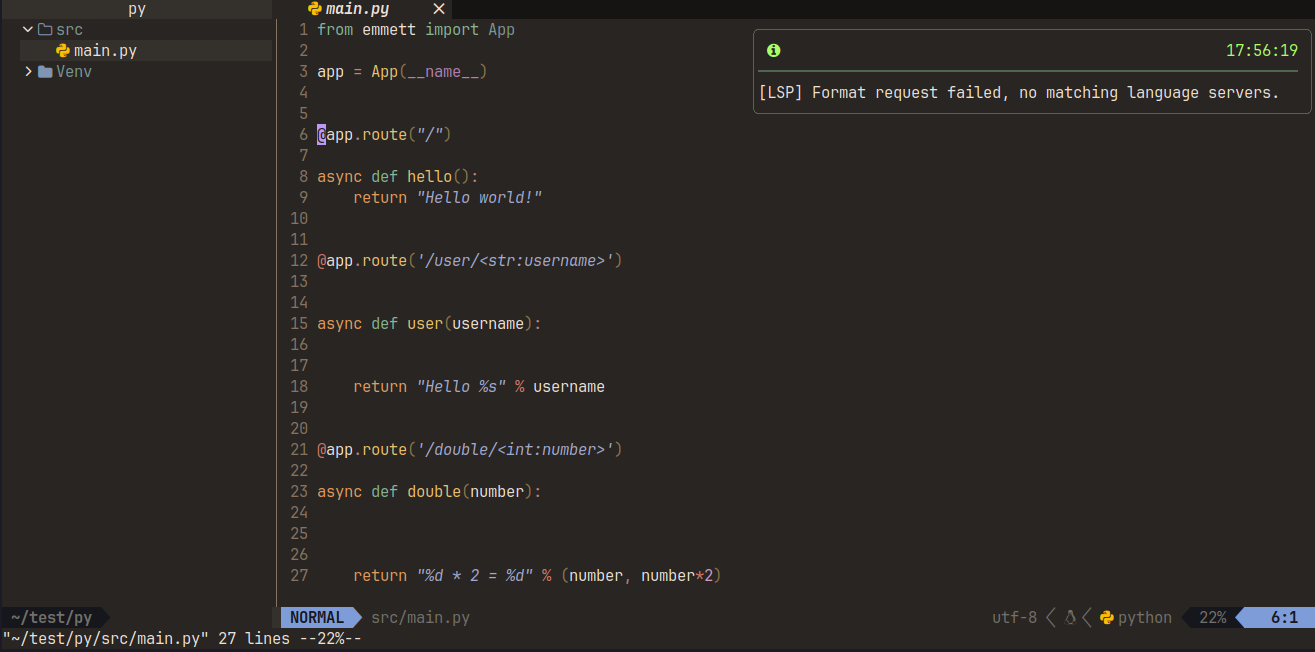
In case mason does not work on your platform
You can manually install the formatters and use the following command :Neoformat click here (opens in a new tab) for more information about Neoformat